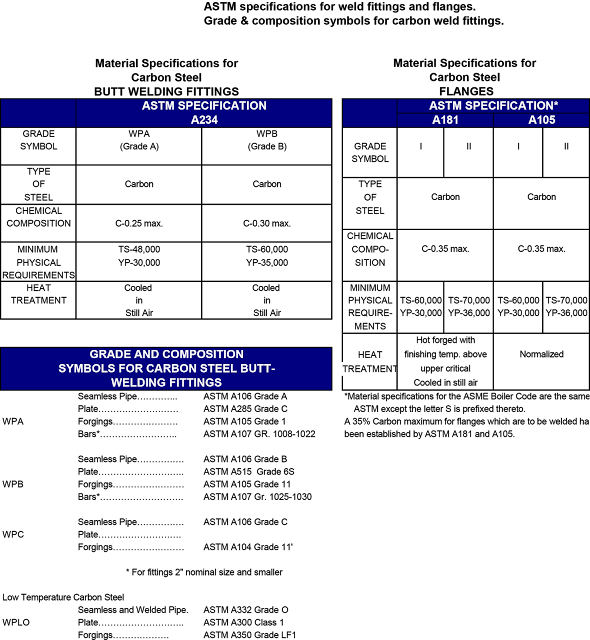
ASME B16.9
Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200).
SCOPE
1.1 General
This Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200).
1.2 Special Fittings
Fittings may be made to special dimensions, sizes,shapes, and tolerances by agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
1.3 Fabricated Fittings
Fabricated laterals and other fittings employing circumferential or intersection welds are considered pipe fabrication and are not within the scope of this Standard.
Fabricated lap joint stub ends are exempt from the above restrictions, provided they meet all the requirements of the applicable ASTM material specification listed in section 5.
1.4 Standard Units
The values stated in either metric or U.S. Customary units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the U.S. Customary units are shown in parentheses.The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this Standard.
The designation for size is NPS for both metric- and customary-dimensioned fittings. Fitting pressure rating is associated with the connecting wall thickness of pipe of equivalent size and material.
1.5 References
Measuring the out diameter
1.5.1 Referenced Standards. Standards and specifications adopted by reference in this Standard are shown in Mandatory Appendix II. It is not considered practical to identify the specific edition of each standard and specification in the individual references. Instead, the specific edition reference is identified in Mandatory Appendix II. A product made in conformance with a prior edition of referenced standards and in all other respects conforming to this Standard will be considered to be in conformance.
1.5.2 Codes and Regulations. A fitting used under the jurisdiction of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, the ASME Code for Pressure Piping, or a governmental regulation is subject to any limitation of that code or regulation. This includes any maximum temperature
limitation, or rule governing the use of a material at low temperature.
1.6 Service Conditions
Criteria for selection of fitting types and materials suitable for particular fluid service are not within the scope of this Standard.
1.7 Welding
Installation welding requirements are outside the scope of this Standard.
1.8 Quality Systems
Nonmandatory requirements relating to the fitting manufacturer’s Quality System Program are described in Nonmandatory Appendix A.
1.9 Convention
For the purpose of determining conformance with this Standard, the convention for fixing significant digits where limits (maximum or minimum values) are specified shall be rounded off as defined in ASTM E 29. This requires that an observed or calculated value shall be rounded off to the nearest unit in the last righthand digit used in expressing the limit. Decimal values and tolerances do not imply a particular method of measurement.
1.10 Pressure Rating Designation
Class, followed by a dimensionless number, is the designation for pressure–temperature ratings. Standardized designations for flanges per ASME B16.5 referenced in this Standard are Classes 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500,and 2500.